[How-To] - Fixing OpenVAS-PostgreSQL errors on install
BACKGROUND
OpenVAS is an open-source vulnerability scanner, which helps cybersecurity professionals to find vulnerabilities present in a computer system or in a network of computers. It’s a great tool and more information about it can be found here. On a Kali Linux system, this scanner can be installed directly from the Kali official repositories using the APT package manager like so:
$ sudo apt update
$ sudo apt install -y openvas
ERROR
To actually get started with using it, there are some prerequisite setup steps that have to be done for it to function as expected. Luckily, there is a handy setup command that one can run to do all this.
$ sudo gvm-setup
This command basically downloads a list of vulnerability information from the GVM remote database, which is used as a reference when scanning for computer vulnerabilities. It also handles creating admin user credentials and other default settings of the scanner.
As part of the setup process, some of the information generated during setup has to be saved and persisted somewhere of course, right? Well, to do that, OpenVAS uses PostgreSQL as the database backend to do just that. However, sometimes things go wrong and an error, like the one below, shows up.
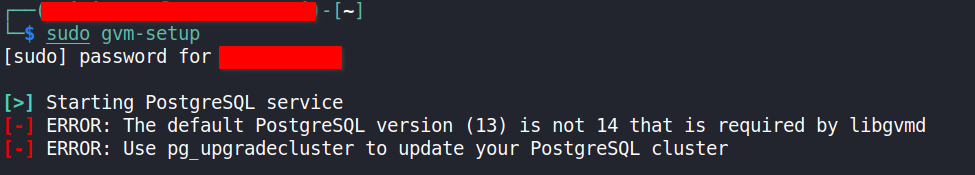
The error indicates that an unsupported version of PostgreSQL is running, and version 14 is the version required for the setup to work as expected. Checking the running clusters of PostgreSQL gives us this.
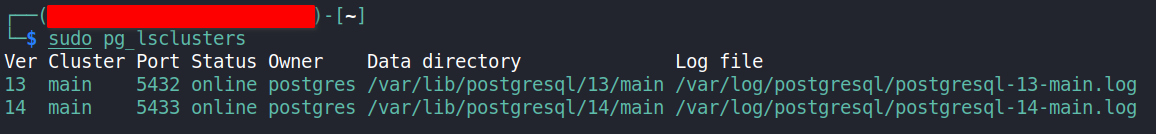
This means that the supported version is actually installed and running on the host Kali machine, but it’s running on a different port from the default port of 5432 for PostgreSQL. So, in this how-to, this shall be fixed by taking the suggestion in the error message i.e. upgrading the cluster to the supported version.
FIX
So, to deal with this, the “newer” cluster needs to first be destroyed i.e. the Ver 14 cluster, and then the Ver 13 cluster can be migrated to Ver 14, as desired by OpenVAS. That is done like so:
$ sudo pg_dropcluster --stop 14 main
$ sudo pg_upgradecluster 13 main /var/lib/postgresql/14/main
Running the second command produces the following message at the bottom of its output.
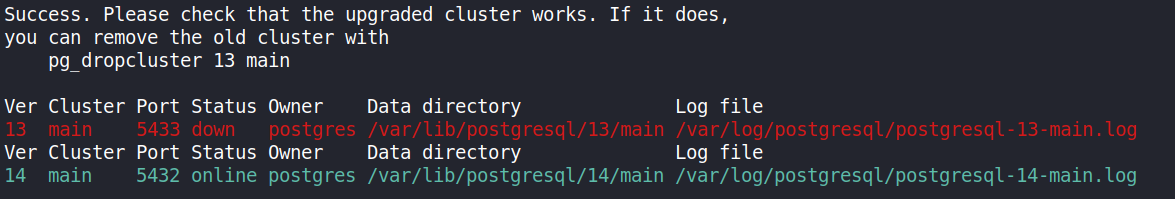
Looking at the message, it shows that the desired cluster is running on the default port for PostgreSQL. But to persist this port change, the new cluster’s configration must be adjusted as well to match the running configuration. To do that, the /etc/postgresql/14/main/postgresql.conf file can be edited like so:
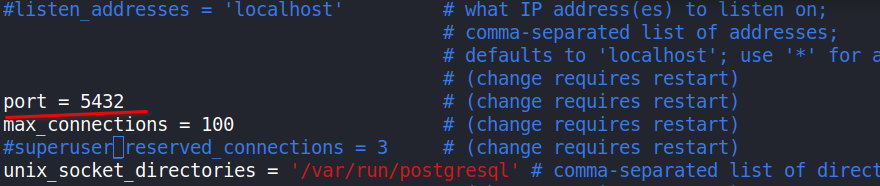
At this point, the fix is complete! Great!
So to validate that the fix was successful, the gvm-setup command needs to be run again to see that it proceeds without a hitch. Once that’s done, the OpenVAS scanner can be started and logged into to perform scans as needed.
$ sudo gvm-setup
$ sudo gvm-start
Queue the “Bob the Builder” theme song! Peace out!